Anatomy:

- Circle of Willis is supplied by the carotids (anterior circulation) + vertebrals (posterior circulation).
- On the RIGHT the CCA originates from the BRACHIOCEPHALIC TRUNK.
- On the LEFT the CCA originates from the AORTIC ARCH directly.
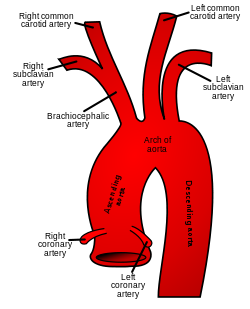
- The points of origin are infrequent points for plaque formation.
- Stenosis most frequently occures at the level of bifurcation of the CCA into ICA and ECA.
- The first intracranial branch of the ICA is the ophtalmic artery.
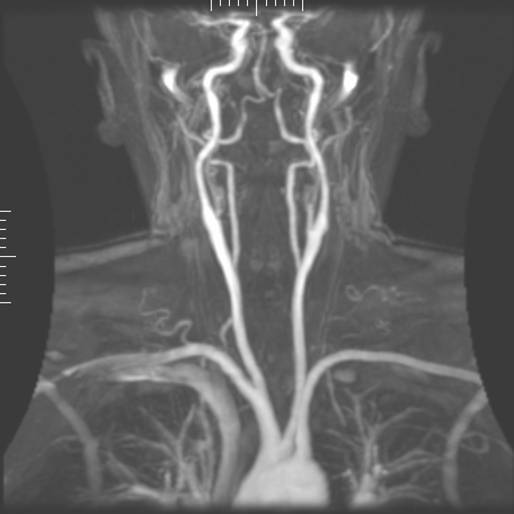
- The vertebral artery (supplying the post. circulation of the circle of Willis) usually arises from the subclavian artery, see below:

- The vertebral artery is divided into 5 segments ( not important for us in examining the carotids).
- The vertebral artery maybe hypoplastic in certain segments, and its usually more prominent on one side.
- The vertebral arteries unite to form the barilar arteries -> circle of Willis -> posterior cerebral artery.
What is subclavian steal syndrome?
In Subclavian steal syndrome (SSS) a reduced quantity of blood flows through the proximal subclavian artery. As a result, blood travels up one of the other blood vessels to the brain (the other vertebral or the carotids), reaches the basilar artery or goes around the cerebral arterial circle and descends via the (ipsilateral) vertebral artery to the subclavian (with the proximal blockage) and feeds blood to the distal subclavian artery (which supplies the upper limb and shoulder).
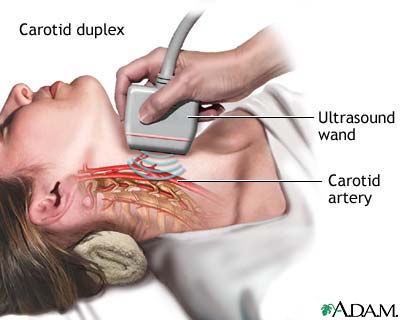
Scaning the carotids:
- ICA PSV is less than 125 cm/sec and no plaque or intimal thickening is visible sonographically.
- additional criteria include ICA / CCA PSV ratio < 2.0 and ICA EDV < 40 cm/sec.
- ICA PSV is less than 125 cm/sec and plaque or intimal thickening is visible sonographically.
- additional criteria include ICA / CCA PSV ratio < 2.0 and ICA EDV < 40 cm/sec.
- ICA PSV is 125 - 230 cm/sec and plaque is visible sonographically.
- additional criteria include ICA / CCA PSV ratio of 2.0 - 4.0 and ICA EDV of 40 - 100 cm/sec.
- ICA PSV is greater than 230 cm / sec and visible plaque and luminal narrowing are seen at gray-scale and color Doppler US (the higher the Doppler parameters lie above the threshold of 230 cm/sec, the greater the likelihood of severe disease).
- additional criteria include ICA / CCA PSV ratio > 4 and ICA EDV > 100 cm/sec.
- velocity parameters may not apply, since velocities may be high, low, or undetectable.
- diagnosis is established primarily by demonstrating a markedly narrowed lumen at colour or power Doppler US (35).
- no detectable patent lumen at gray-scale US and no flow with spectral, power, and colour Doppler US.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Carotid arterial disease can be conveniently graded into percentage stenoses by assesing several sonographic parameters. The NASCET criteria is as follows.
- no stenosis : normal wave form
- < 15 % stenosis :
- deceleration spectral broadening with a peak systolic velocity (PSV) of < 125cm/s
- 16 - 49 % stenosis :
- pan-systolic spectral broadening with a peak systolic velocity (PSV) of < 125 cm/s
- 50 - 69 % stenosis :
- pan-systolic spectral broadening with a peak systolic velocity (PSV) of > 125 cm/s and
- end diastolic velocity (EDV) < 110 cm/s or
- ICA/CCA PSV ratio > 2 but < 4
- 70 - 79 % stenosis :
- pan-systolic spectral broadening with PSV > 270 cm/s or
- EDV > 110 cm/s or
- ICA/CCA PSV ratio > 4
- 80 - 99% stenosis : EDV > 140 cm/s
- complete occlusion : no flow : terminal thump
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
LINKS:
Video:
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yuKu_6RhNOM
(Text source: Teaching atlas of CDS-Thieme, wikipedia)
(Images: google pictures)
No comments:
Post a Comment