Hemangioma in the live:
In the 7th segment of the liver, a 13 mm rounded echogenic area is seen, elsewhere the liver is homogeneous.
- Dont`t confuse with focal fatty infiltration of the liver usually seen arround the GB, or the echogenic ligamentum teres.
- Dont`t confuse with focal fatty infiltration of the liver usually seen arround the GB, or the echogenic ligamentum teres.
- A hemangioma can be echogenic or isoechoic.
- Smooth margins, round or oval in shape.
- Often multiple, may contain calcifications, rarely has a peripheral rim.
- Unlike FNH hemangiomas are vascularised in a peripheral-to-central pattern => aka iris diaphragm sign.
CEUS:
Arterial phase (20-30 sec): outer portions enhance, center remains hypoechoic.
Portal phase (40-100 sec): central portions become increasingly echogenic.
Venous phase (110-180 sec): the entire leasion is hypoechoic.
LINKS:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
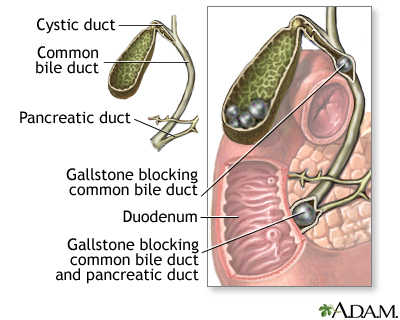
 Hepatic cyst
Hepatic cyst




























Differential diagnosis for cystic leasions:
inflammatory, infectious (echinococciasis, abscess), traumatic (hematoma), neoplastic (cyst-like mets, regressive necrotic liquified mets).
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Echinoccocal cyst: anechoic, round, echogenic wall, calcifications in cystic echinococcosis.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Hematoma: irregular in shape, no wall, has low level internal echos


Traumatic liver rupture with hematoma

Subcapsular hematoma - US

Subcapsular hematoma - CT
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Abscess: irregular in shape, no wall, internal echos



-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Cyst-like mets:
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Hepatic tumors

A: Illustration of morphologic patterns of hepatic tumors in the B-mode ultrasonography; B: Illustration of enhancement patterns of hepatic tumors in the arterial phase
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
HYPOECHOIC CHANGES:
Focal sparing in fatty infiltration:
- Mostly seen in periportal region next to GB or lig. Trias
- Elliptical or triangular
- May occasionally show a patchy or flame like distribution in the liver



-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Focal Nodular Hyperplasia
- The 2nd most common bening liver tumor after hemangioma
- It is usually asymptomatic, rarely grows or bleeds, and has no malignant potential. This tumour is often resected because it is difficult to distinguish from hepatic adenoma.
- Hypoechoic round or elliptical
- Smooth margins
- Heterogeneous echo-pattern due to central scarring
- Echogenic extensions radiating to periphery (stellate scar)
- CDS: vessels passing through the radial connective tissue (spoked wheel pattern) 








-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Adenoma:
- Resembles FNH in B mode US
- Made up from hepatocytes, and vessels
- Isoechoic or hypoechoic
- Smooth margins
- Pseudocapsule or hypoechoic rim
- Small internal echos if has hemorrhage
- CDS: well vascularised, characteristic vascular pattern, feeding artery can be seen



-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC):
-Variable appearance
- Hypoechoic, isoechoic, hyperechoic, nonhomogeneous
- Solitary or isolated
- In cirrhotic liver
- Frequent regressive changes (hemorrhage, calcifications)
- CDS: increased vascularisation, no typical pattern of arrangement



-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Cholangiocellular carcinoma:
- Diffuse growth
- Isoechoic or sometomes hypoechoic (due to scarring)
- Regional mets with ascites

-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Hematologic malignant systemic diseases:
- Micronodular malignant systemic diseases (CML), or macronodular lesions ( high grade lymphomas, lymphogranulomatosis)
- Intensly hypoechoic without a peripheral halo
- Accompanied by othe intra-abdominal sites of LN infiltration
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Other images:


Two hyperechoic leasions in the liver.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
LINKS:
(Text main source: Teaching Manual of CDS-Thieme, Thieme Clinical Companion Ultrasound)
(Images: Pecs University Department of Radiology, google images, ultrasoundcases.info)